Wheels for trolleys: main types and purpose
Wheels for trolleys: varieties and characteristics of models
The trolley wheel is an indispensable structural element, without which the operation of the transport device will be impossible. Such products are produced in a wide range of models and differ primarily in design. Let's figure out which characteristics are the main ones.
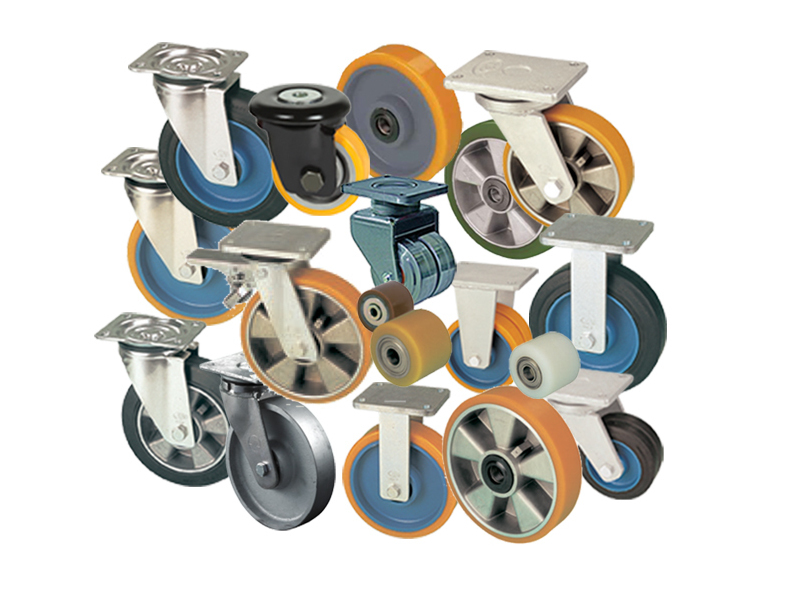

Major differences
The types of trolley wheels form a wide variety of models. They are classified according to the following criteria:
- Appointment.
- Material.
- Carrying capacity.
- Bearing type.
- Features of fastening.
Let's dwell on each point in more detail.

Differences by scope
Depending on the operating conditions, the rollers differ into household and industrial.
The first are models for garden and light wheelbarrows, which are widely used in private households. A distinctive feature is a low carrying capacity (in comparison with industrial ones).
The latter are intended for warehouse equipment. They are installed on transport devices that are used in the field of logistics, in production, in workshops. This category also includes products for trade equipment, which is used when transporting products in stores and shopping centers.
Important: there is another group of industrial models - for special purposes. They are installed on trolleys, which are designed to handle large loads. The endurance of one roller can be up to 7 tons.

Type of material depending on the purpose
The raw materials from which the wheels are made directly affect their use. You need to choose taking into account the type of coverage on which the trolley is planned to move:
- tiled. For such operating conditions, you need to choose polyurethane or rubber products. They dampen vibrations well and are less noisy;
- asphalt. Suitable for such a coating are wheels with a rubber contact layer (thermoplastic or standard), pneumatic models;
- concrete or cement-resin floor. For such conditions, polyamide, rubber or polyurethane models are more suitable;
- soil. The optimal solution is pneumatic or rubber structures;
- industrial self-leveling floors. For such a coating, it is worth choosing polyamide, polyurethane or rubber models;
- slatted floor - pneumatic or polyamide.
Important: be sure to take into account the temperature regime. According to this criterion, the wheels are divided into models suitable for use indoors (0-40 degrees), outdoors (withstand up to -20 °) and heat-resistant (from -50 to +300 and more). The latter are intended for use in freezers or industrial ovens.
Differences in lifting capacity
According to this parameter, 4 categories can be distinguished:
- lungs. They can hold up to 200 kg;
- medium. One such wheel is capable of providing a lifting capacity of up to 400 kg;
- heavy duty. Withstand up to 1100 kg;
- with maximum lifting capacity. One product can withstand up to 7 tons. Such models are installed on heavy warehouse equipment and industrial equipment for loading and unloading and transport operations.
To determine the carrying capacity, you can use the formula: load mass + trolley weight ÷ number of wheels - 1. Minus one wheel is used as a safety net, since during operation there are situations when one of the rollers (or two) loses adhesion to the coating.
Using the link https://www.fregat.com.ua/katalog/, you can choose a suitable configuration option for carts for different purposes. The rollers are available in the Fregat catalog in a wide range of models.
Differences by bearing type
Driving performance and reliability directly depend on this structural element. For completing, they usually use:
- ball;
- roller;
- plain bearings.
The first is the most durable type, characterized by high carrying capacity and endurance. Roller models slow down wheel wear and are easy to maintain. Plain bearings are recommended for light loads and low speed travel.
Differences in the fastening principle
According to this classification, trolley wheels are differentiated between models, which use brackets or do without brackets to fix them. Devices of the second type are used when completing hydraulic and two-wheeled carts, as well as those transport devices in which the wheels are put on the axle.
Rollers with brackets differ in functionality on swivel and non-swivel. The first ones are maneuverable and can rotate around an axis. Available with and without brakes. Fixed ones are responsible for directional stability, provide a straight trajectory of movement of equipment.